FASTA
FASTA is text-based format for representing nucleotide or peptide sequences, where each sequence is preceded by a single-line description starting with a “>” character.

.fnacan be used for nucleotide sequences.faacan be used for amino acid sequences.frncan be used for RNA sequences.facan be used for either nucleotide or amino acid sequences
FASTQ
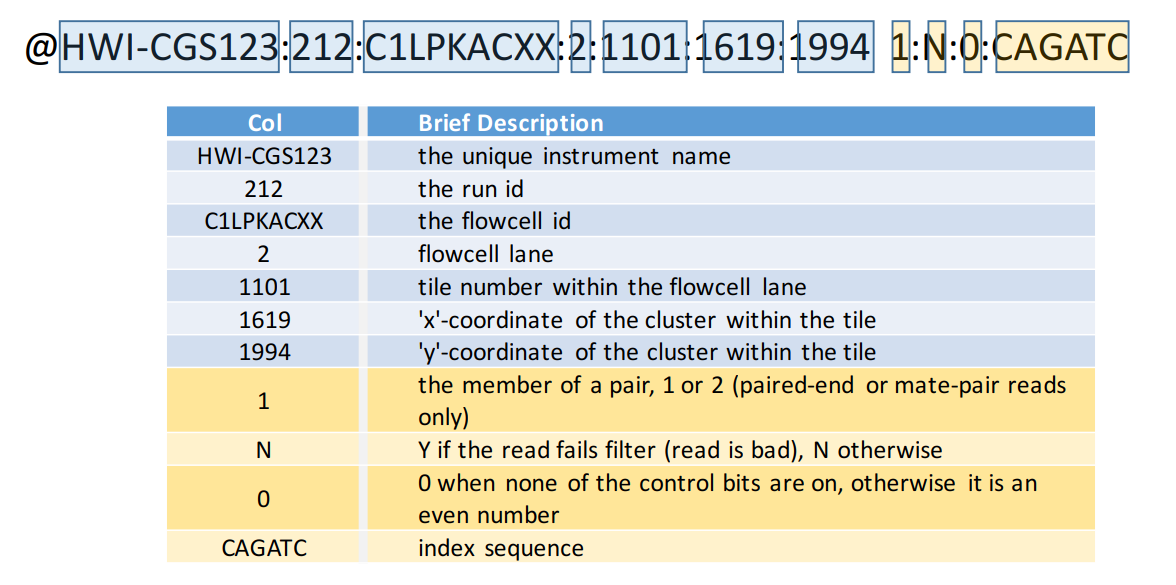
FASTQ format is a text-based format for storing both nucleotide sequences and their corresponding quality scores. Each sequence entry consists of four lines: * a sequence identifier starting with “@” * the raw sequence letters * a “+” separator line * and a line with quality scores encoded as ASCII characters

SAM
SAM: Sequence Alignment Map * Text tab-delimited format * Exome: >50Gb
* Whole genome: 800Gb-‐1Tb
BAM
BAM: Binary Alignment Map * Binary, compressed * Index for quick looking up regions * Exome: 2-20Gb * Whole genome: 100-‐300Gb
CRAM
VCF
Variant Call Format (VCF) is a format for storing variations between a reference genome and sequences aligned to it, based on SAM/BAM alignments. VCF files begin with a header section: lines in the header section begin with ##. The last line in the header section begins with #; this line gives the headers of the columns used in the VCF file:
- VCF Meta-information starts with ## and must be key=value pairs
- Header line starts with #CHROM
- Data lines contain 8 mandatory columns:
- CHROM: Reference
- POS
- ID
- REF
- ALT
- QUAL
- FILTER
- INFO
BCF
GTF
Gene Transfer Format (GTF) is a file format used to hold information about gene structure. It is a tab-delimited text format that consists of 9 columns: 1. seqname: Name of the chromosome or scaffold; chromosome names can be given with or without the ‘chr’ prefix. 2. source: Name of the program that generated this feature, or the data source (database or project name). 3. feature: Feature type name (e.g., Gene, Variation, Similarity). 4. start: Start position of the feature, with sequence numbering starting at 1. 5. end: End position of the feature, with sequence numbering starting at 1. 6. score: A floating point value. 7. strand: Defined as + (forward) or - (reverse). 8. frame: One of ‘0’, ‘1’ or ‘2’. ‘0’ indicates that the first base of the feature is the first base of a codon, ‘1’ that the second base is the first base of a codon, and so on. 9. attribute: A semicolon-separated list of tag-value pairs, providing additional information about each feature.